c语言基础知识复习
编辑器gcc的编辑过程,c源文件->预处理->编译->汇编->链接->可执行文件,每一个步骤都可以通过gcc命令生成相应的文件,查看源文件进行解释,也可以一步进行到底,直接生成最终的文件。
注释小技巧
在c语言中除了经常使用的//与/*注释之外,还可以使用#if 0 进行配合使用,完成注释的效果
类型比较的注意点
精度类型比较
在c语言中存在许多的类型,但是在比较的时候,int类型与float类型进行比较可能会发生结果不准确的情况,因为float类型只能精确表示到6位的数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main(void){
float a=0.000000001;
float b=a-0;
printf("%f\n",b);
bool flag=(b==0);
printf("%d\n",flag);
}
|

常量与变量
常量
常量我们可以分为整型常量、实型常量、字符常量、与标识常量
- 整型常量:1,790,65等等
- 实型常量:3.14,5.23,1.5689等等
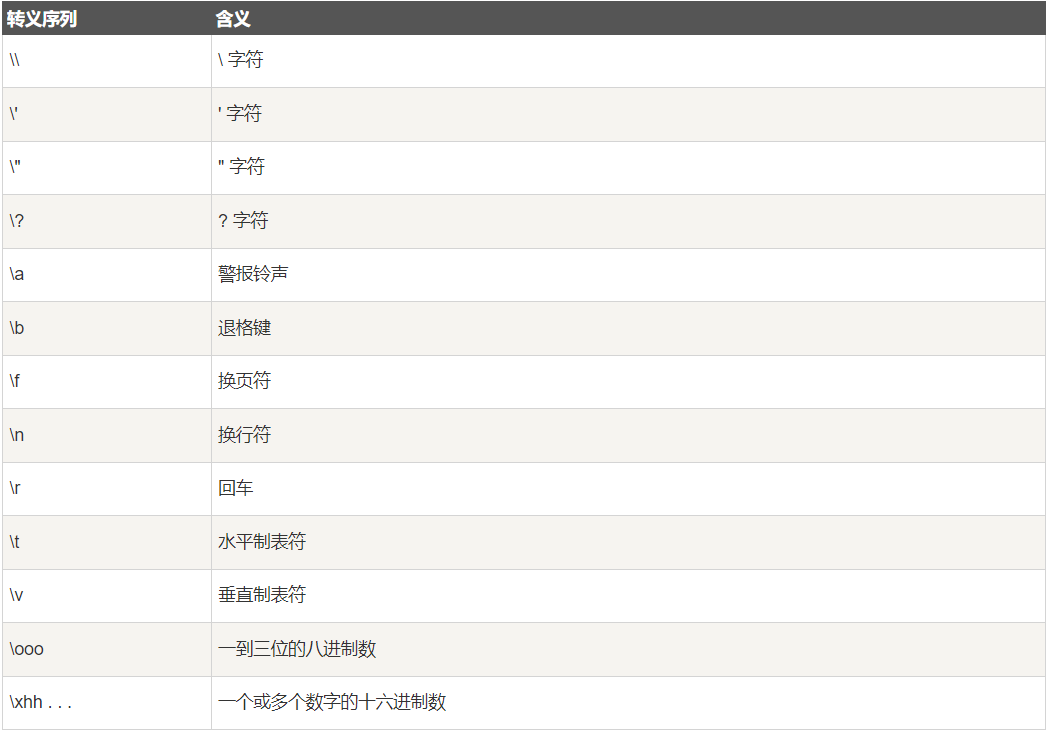
- 字符常量:由单引号引起来的单个字符或者转义字符,比如’a’,’b’,’\t’,注意这里的字符常量也可以表示8进制数,比如\ddd表示3位8进制数,而\xxh表示2位16进制数,那么此时‘015’是合法的,但是’018’却是不合法的,超出8进制的表示范围
- 字符串常量:由双引号引起来的一个或者多个字符进行实现的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
int main(void){
int a=1;
printf("%d\n",a);
float b=2.3;
printf("%f\n",b);
char c='\011';
printf("%o\n",c);
char d[10]="sdvgws";
printf("%s",d);
}
|

变量
类型的定义:[存储类型] 数据类型 标识符 =值
而数据类型=基本数据类型+构造类型
存储类型:auto static register
而auto是我们的默认的类型,自动分配空间,自动回收空间
而register:表示为寄存器类型,会把值放到寄存器中,如果使用的次数比较多,可以添加这种类型,但是寄存器也会考虑是否将此值放入到其中,一般是局部变量等等限制
static:静态类型变量,此值具有继承性
extern:说明性关键字,不能改变被说明的变量的值或者类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| #include <stdio.h>
void fun();
int main(void){
fun();
fun();
fun();
}
void fun(void){
static int i=0;
i++;
printf("%d\n",i);
}
|
而static在修饰函数的时候,那么此函数就不能被其他的文件中的函数调用,与Java中的private相似,达到了封装的效果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
#include "stdio.h"
#include "pro.h"
static void fun(void ){
printf("我是静态的static函数");
}
void call_fun(void){
fun();
}
|
define的使用
注意点
在使用define使用的时候,c语言在预处理的时候就已经将其替换为相应的数字,而且使用与更改更加方便,此时只是将宏体替换为宏名称,并不会进行语法检查
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
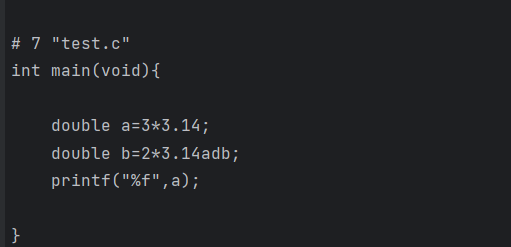
| #include <stdio.h>
#define PI 3.14
#define PI1 3.14adb
int main(void){
double a=3*PI;
double b=2*PI1;
printf("%f",a);
}
|
看上面的代码,我们可以看出来PI1其实是错误的,但是最终编译之后的代码并不会给出这个错误,仅仅是实现了宏替换,执行gcc -e 程序名称
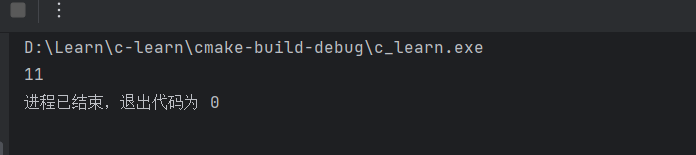
现在我们在进行一个例子,继续进行相关的操作,我们的想要的结果应该为5*5,但是最终的结果为11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| #include <stdio.h>
#define ADD 2+3
int main(void){
printf("%d",ADD*ADD);
}
|
我们继续看这个编译之后的情况,可以看到,这个define仅仅是进行了替换,但是我们所预想的括号并不存在
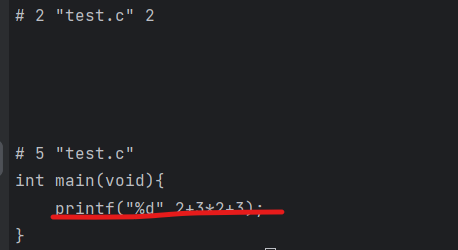
其他用法
其实宏定义还可以定义一个类似函数的功能,但是还是拥有许多的陷阱,比如下面的结果中为什么,最大值成为8了,而不是7??
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| #include <stdio.h>
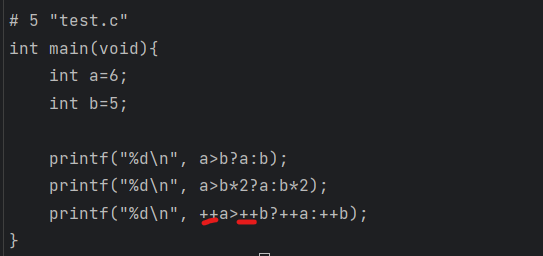
#define MAX(a,b) a>b?a:b
int main(void){
int a=6;
int b=5;
printf("%d\n", MAX(a,b));
printf("%d\n", MAX(a,b*2));
printf("%d\n", MAX(++a,++b));
}
|
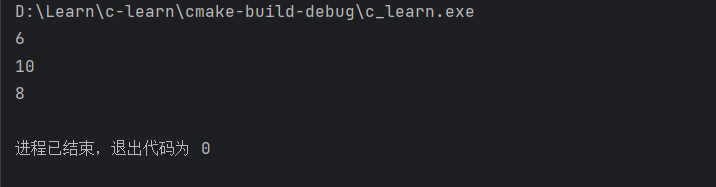
我们仔细看一下这个中间的执行过程,可以发现其实最大的值执行了两次
输入与输出
标准的输入与输出
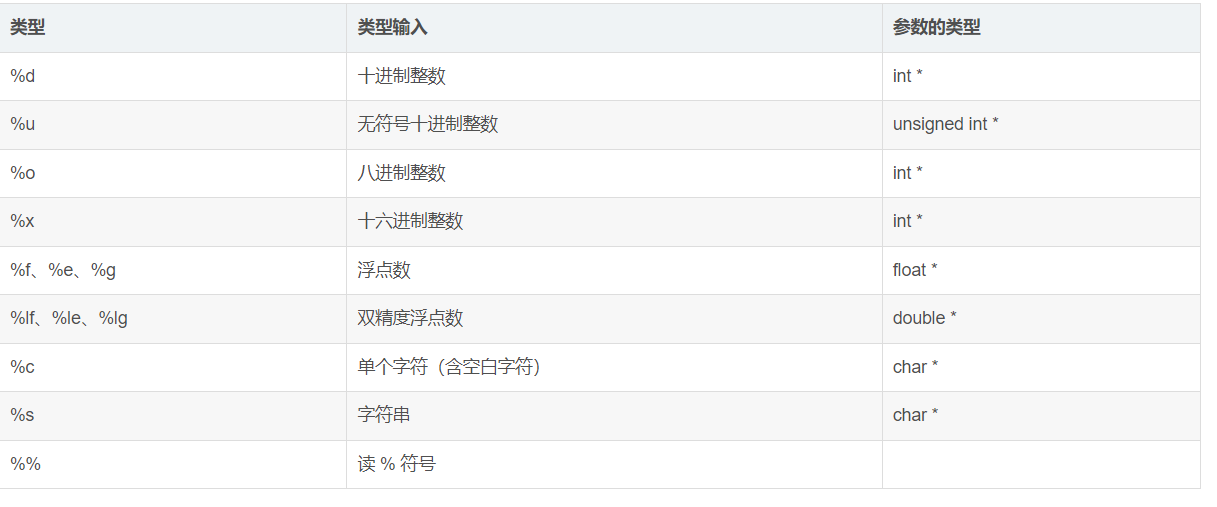
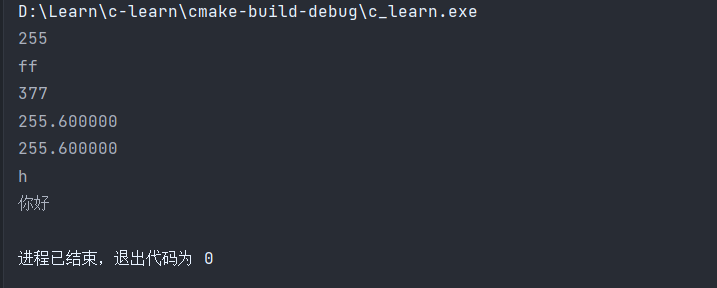
printf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| #include "stdio.h"
int main(void){
printf("%d\n",255);
printf("%x\n",255);
printf("%o\n",255);
printf("%f\n",255.6);
printf("%c\n",'h');
printf("%s\n","你好");
}
|
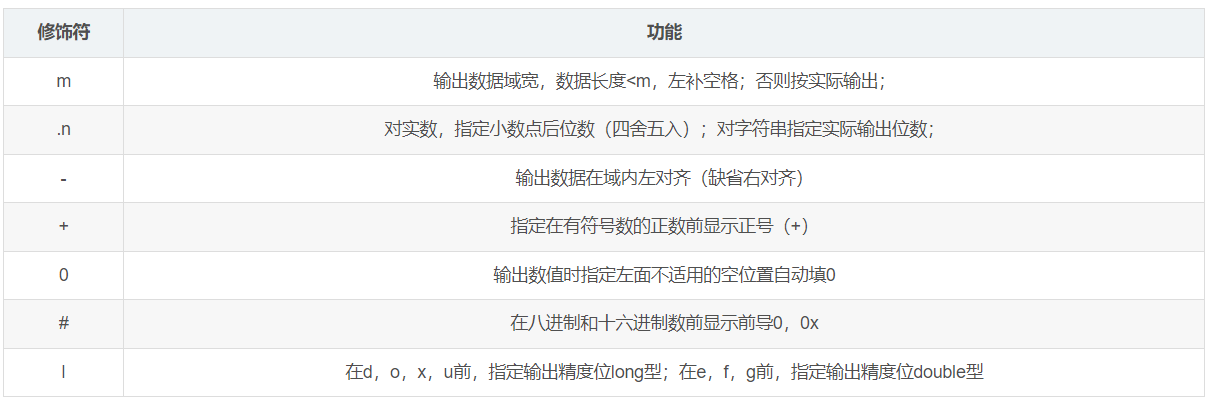
而同样在输出的时刻,我们也可以对这些数字进行格式化操作输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| #include "stdio.h"
int main(void){
printf("%4d\n",255);
printf("%.2f\n",255.6986);
printf("你好%-10d\n",56);
printf("你好%10d\n",56);
printf("%#o\n",255);
printf("%#x",255);
}
|
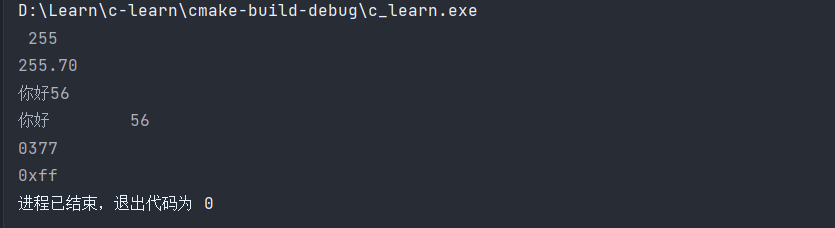
小注意点
我们在进行输出的时候,最好能够加上\n的换行操作,此换行符具有刷新缓冲区的功能观察下面的两段程序,发现死循环之前的语句也没有打印出来
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| #include "stdio.h"
int main(void){
printf("开始循环");
while (1);
printf("结束循环");
}
|
scanf函数
scanf函数默认遇到空格就自动结束,并将剩余的输入保存到下一个缓冲区,可以看到我们下面str1其实没有经过输入便接受了值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| #include "stdio.h"
int main(void){
int i;
printf("请输入一个数值\n");
scanf("%d",&i);
printf("i=%d\n",i);
printf("请输入一个字符串\n");
char str[32];
scanf("%s",str);
printf("str=%s",str);
char str1[32];
printf("请输入下一个字符串\n");
scanf("%s",str1);
printf("str1=%s",str1);
}
|
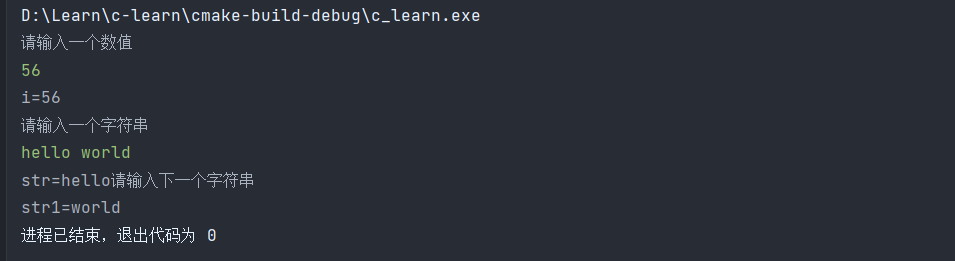
注意scanf函数的返回值是代表成功输入的个数,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| #include "stdio.h"
int main(void){
int i;
int j;
printf("请输入两个数值\n");
int ret=scanf("%d%d",&i,&j);
printf("ret=%d\n",ret);
}
|
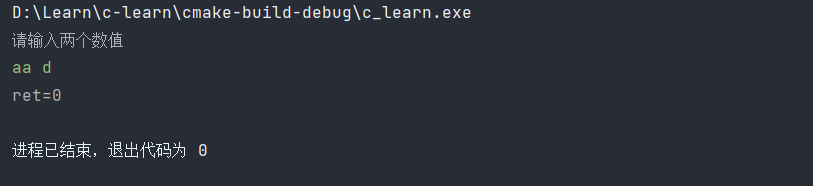
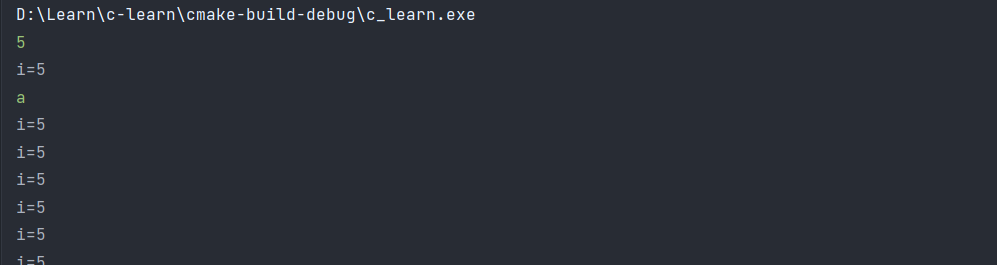
也就是说,我们在循环的时刻,一定要判断我们输入的值是否正确被接受,否则会一直循环执行取出缓存中的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| #include "stdio.h"
int main(void){
while (1){
int i;
scanf("%d",&i);
printf("i=%d\n",i);
}
}
|
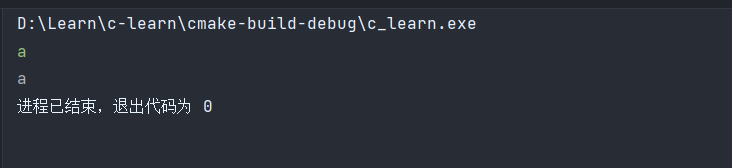
getchar与putchar
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| #include "stdio.h"
int main(void){
int ch;
ch=getchar();
putchar(ch);
return 0;
}
|
gets与puts
注意gets是一个非常危险的函数,在这里如果我们输入的字符串已经发生了越界,但是仍旧不会给予警告错误,下面的其实已经越界但是仍旧输出。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| #include "stdio.h"
#define STRSIZE 6
int main(void){
char str[STRSIZE];
gets(str);
puts(str);
return 0;
}
|
而其实我们一般会使用fgets进行代替,但是fgets也是有一些缺陷的,他只是保证我们不会出错,但是并不会完全接受我们的这一行值,我们可以使用getline进行实现
1
| char * fgets (char *__restrict, int, FILE *__restrict);
|


















